What is a Clean Fuel Standard?
A clean fuel standard, also called a low carbon fuel standard or a clean fuel policy, is a technology-neutral, performance-based policy that reduces the use of high-carbon transportation fuels while providing incentives to deploy lower-carbon fuels such as electricity, hydrogen, biofuels, propane, and natural gas.
What are some of the benefits of a Clean Fuel Standard?
A clean fuel standard is a proven policy to deploy more clean fuels and at the same time create economic and environmental benefits. Benefits of a clean fuel standard include:
- Increasing access to lower-carbon (and often lower-cost) transportation fuels for individuals and fleets
- Net-positive economic benefits like growing the gross domestic product (GDP) and the number of clean mobility jobs
- Strengthening state leadership and innovation by facilitating increased investments in a portfolio of cleaner fuels
- Reducing harmful emissions across transportation, electricity, and agriculture sectors, resulting in cleaner air and improved public health outcomes
- Supporting domestic fuels and increasing energy independence, which keeps energy dollars in our local communities
- Incentivizing lower emissions throughout fuel supply chains, including rewarding farmers who practice climate-friendly farming
How does the policy work?
At the most basic level, a clean fuel standard sets a requirement for reducing the average carbon intensity of transportation fuels over time.
Carbon intensity is measured in grams of carbon dioxide equivalent per megajoule (g CO2e / MJ) and incorporates all emissions in the fuel’s “well-to-wheels” lifecycle, including production, conversion, and use. Carbon intensity values are assigned to both conventional fuels, like gasoline and diesel, as well as lower-carbon fuels, such as biodiesel, electricity, ethanol, hydrogen, renewable diesel, renewable natural gas, renewable propane, and others.
Electricity for electric vehicles has a different score based on the mix of resources used to produce electricity. Similarly, the scores for liquid fuels vary based on factors like the farming practices used to create feedstocks, energy used at the processing plant, and more.
A clean fuel standard also sets a timeline for required emissions reductions in the transportation sector. For example, the policy could require a 15 percent carbon intensity reduction over a 10-year period, with yearly carbon reduction targets. The yearly targets are the carbon intensity standard (sometimes called the performance standard) and what fuels will be measured against.
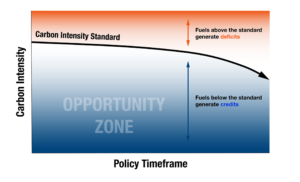 Figure authored by Elizabeth Abramson, GPI, 2020
Figure authored by Elizabeth Abramson, GPI, 2020
How do credits work?
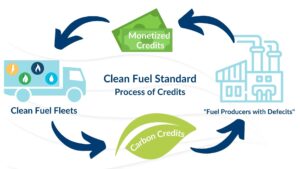
Fuels with carbon intensities higher than the performance standard generate deficits, while fuels with carbon intensities below the standard generate credits. To comply with the standard, fuel producers with deficits must blend low-carbon fuels with the petroleum products they make or purchase credits from other fuel producers.
Credits have a market value (typically measured in $/ton of greenhouse gas emissions), which varies based on the performance standard and market forces. Once a credit is used to cover a deficit, it is retired.
The policy framework and credit market determine how credits are allocated and distributed to different entities involved in the fuel lifecycle, from production to distribution and consumption.
Does Michigan have a Clean Fuels Standard?
Michigan currently does not have a clean fuel standard. However, Senate Bill 275 and House Bill 5083 have been introduced to create one. There are models across North America that Michigan can follow to create our own version of the clean fuel standard.
Clean Fuels Michigan is working with more than 60 stakeholders to explore the opportunity to implement a clean fuel standard in Michigan. To get involved or for more information, check out the Michigan Clean Fuel Standard Coalition website or reach out to Jane at jmccurry@cleanfuelsmi.org.
Many thanks to the Great Plains Institute for letting us borrow from their extensive collection of Clean Fuel Standard resources to create this blog.
